Time Constant First Order System
Time constant first order system. Determine the time when the signal has decayed to 37 of the initial value. This is true of all first order systems. Consider the equation C s 1 s T 1 R s Substitute R s value in the above equation.
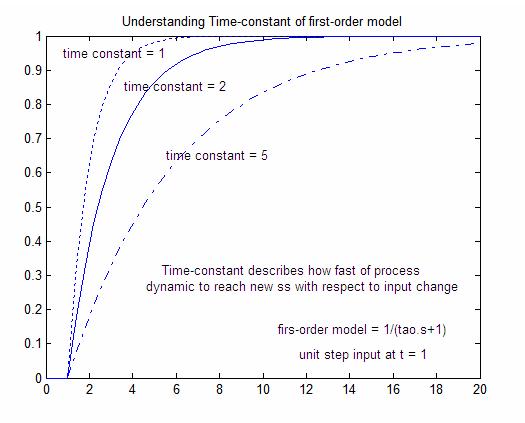
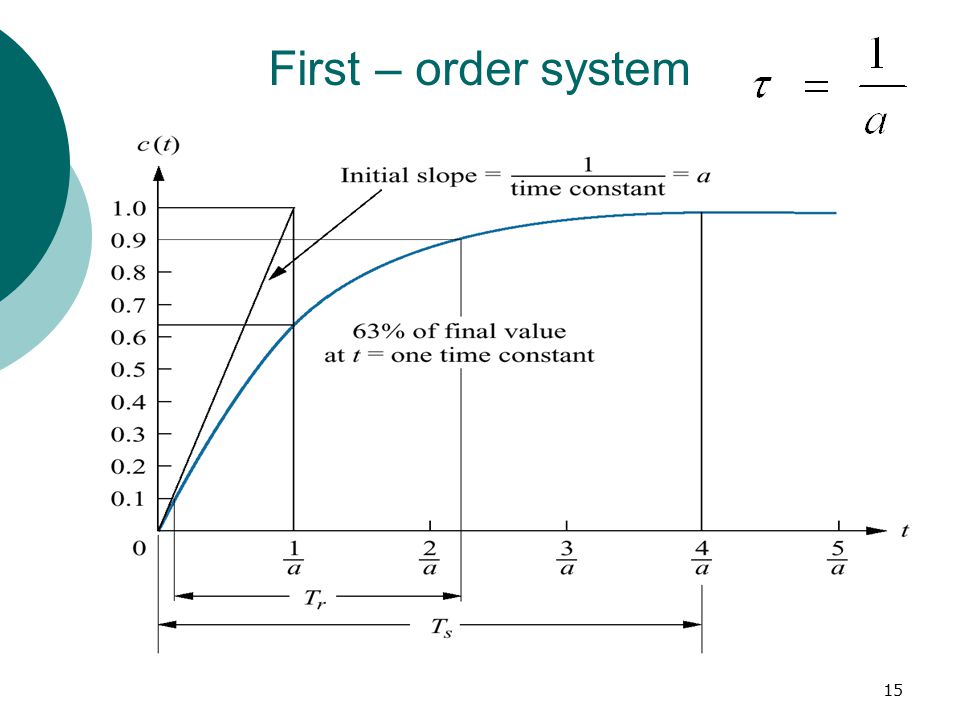
If time constant is larger system goes to move slow. The time constant is given by T 1 ζ ω n. How can I find the time constant of a first order system transfer function.
Comparative study of PID controlled modes on automatic water level measurement system. T s K sτ 1 T s K s τ 1. Time response of first order system with unit ramp signal is - Now putting the value of RS in the equation.
Now the question is to find time constant as well as DC gain so I can find its transfer function. Refers to the time required for the physical quantity to decay from the maximum value to 1e of the maximum value. As t increases it takes longer for the system to respond to the step disturbance.
Now taking the inverse Laplace of the above equation. For example a resistor-capacitor circuit in an electronic amplifler might have a time constant of a few microseconds while the cooling of a building after sunset may be described by a time constant of. 2 ζ ω n b c and ω n 2 a b c.
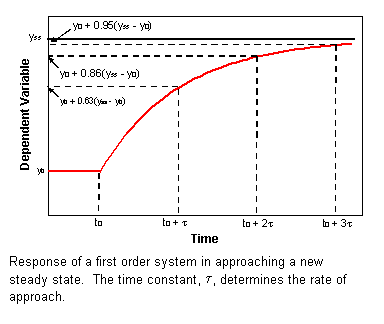
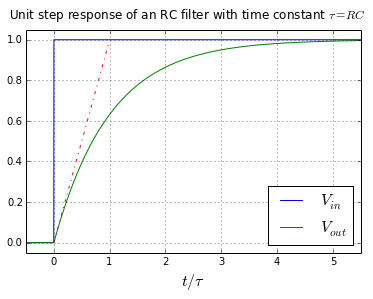
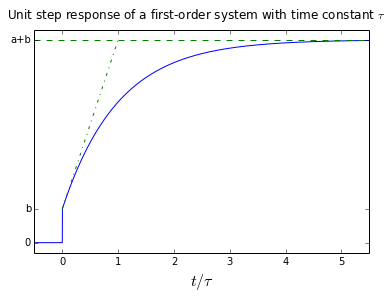
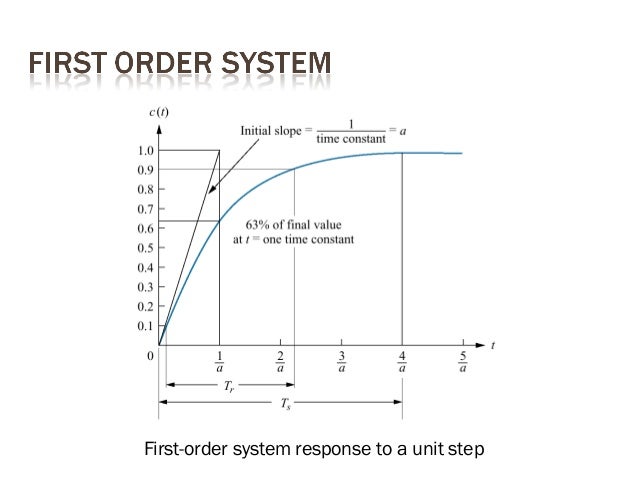
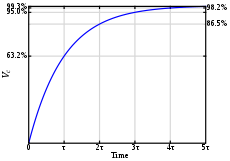
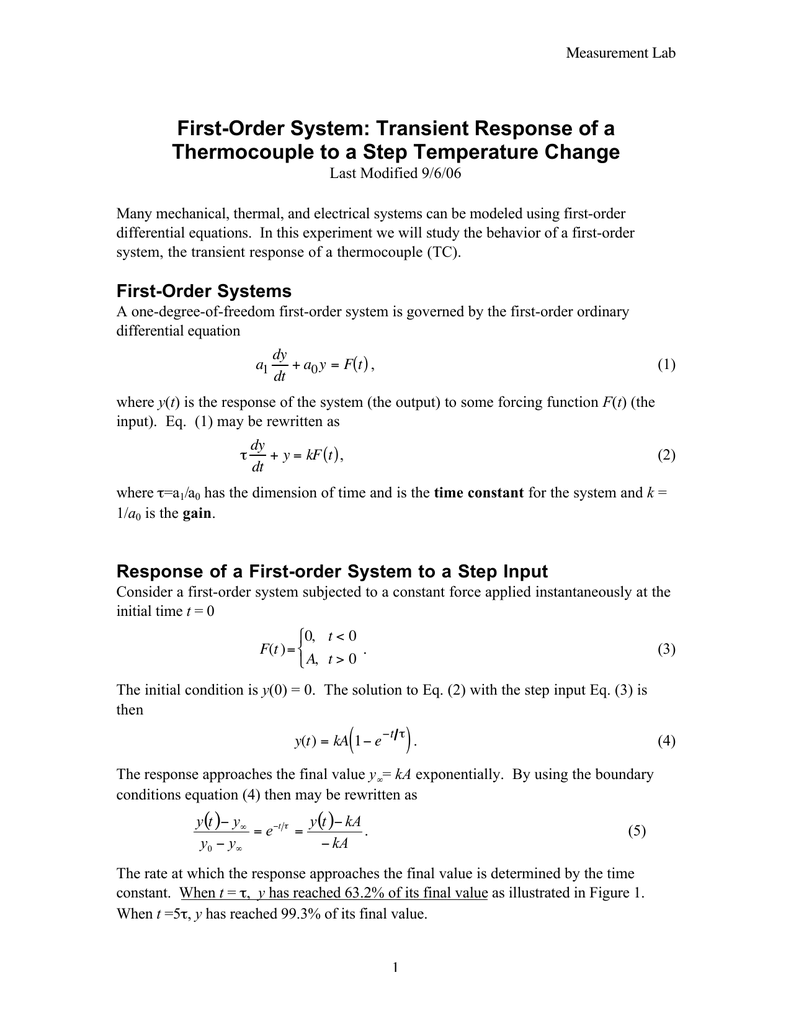
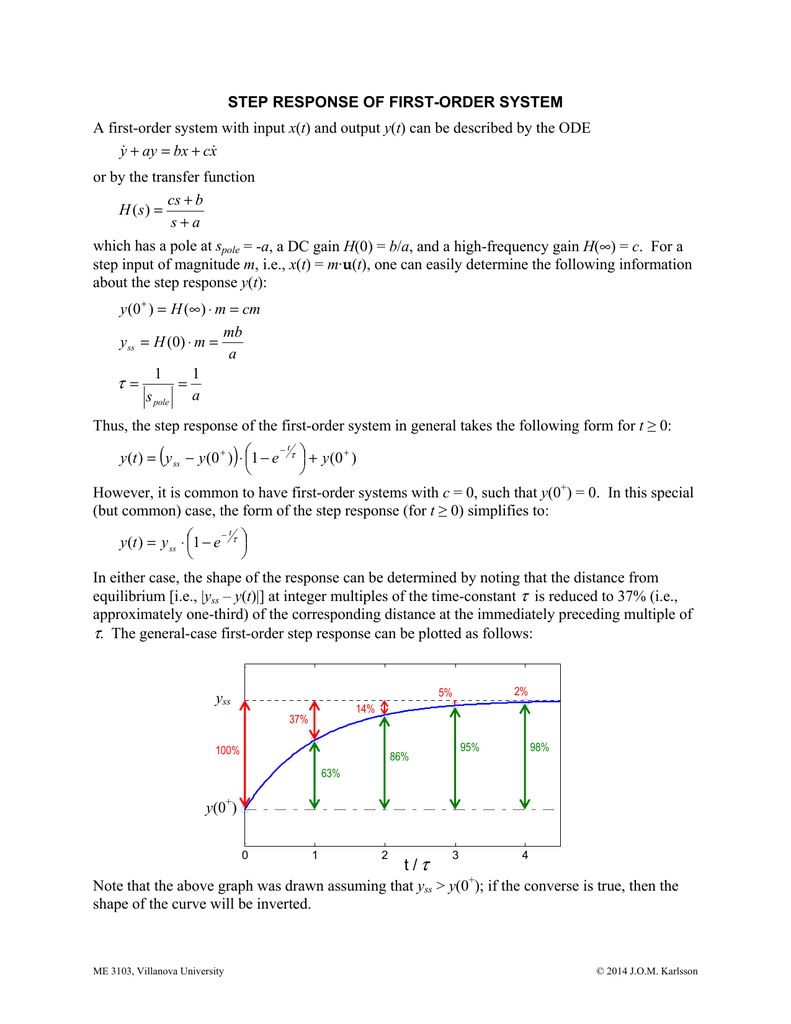
The step response of the system is the response for a step of input voltage. Physically the time constant represents the elapsed time required for the system response to decay to zero if the system had continued to decay at the initial rate because of the progressive change in the rate of decay the response will have actually decreased in value to 1 e 368 in this time say from a step decrease. Determine the initial value of the signal y0 as above.
In practice a common unit is rpmV where rpm refers to revolutions-per-minute. The elapsed time is the time.
Comparative study of PID controlled modes on automatic water level measurement system.
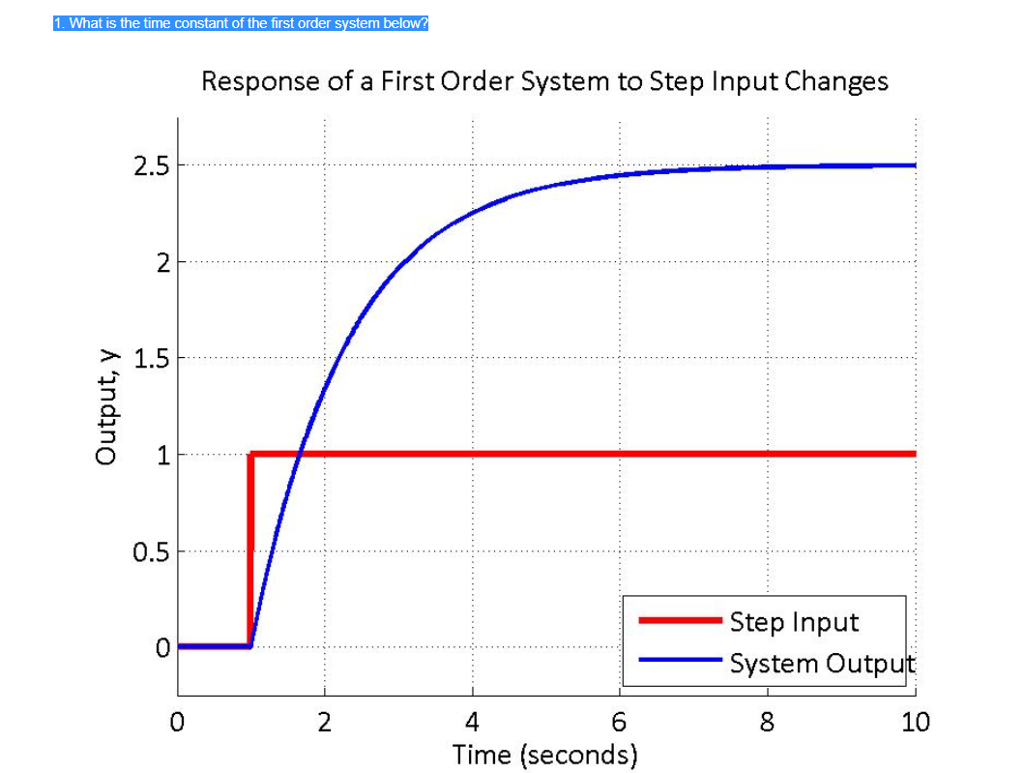
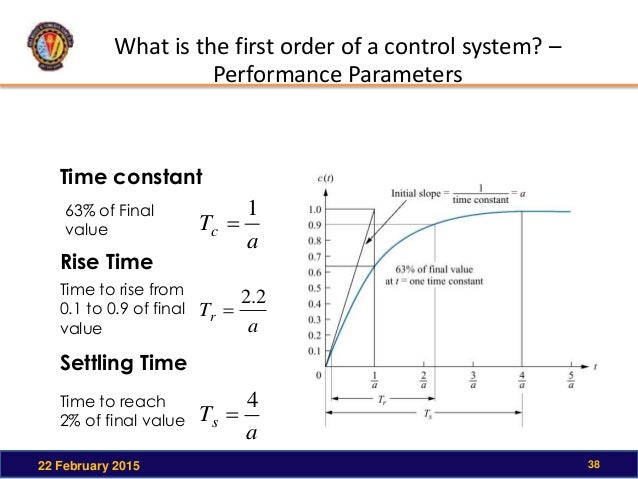
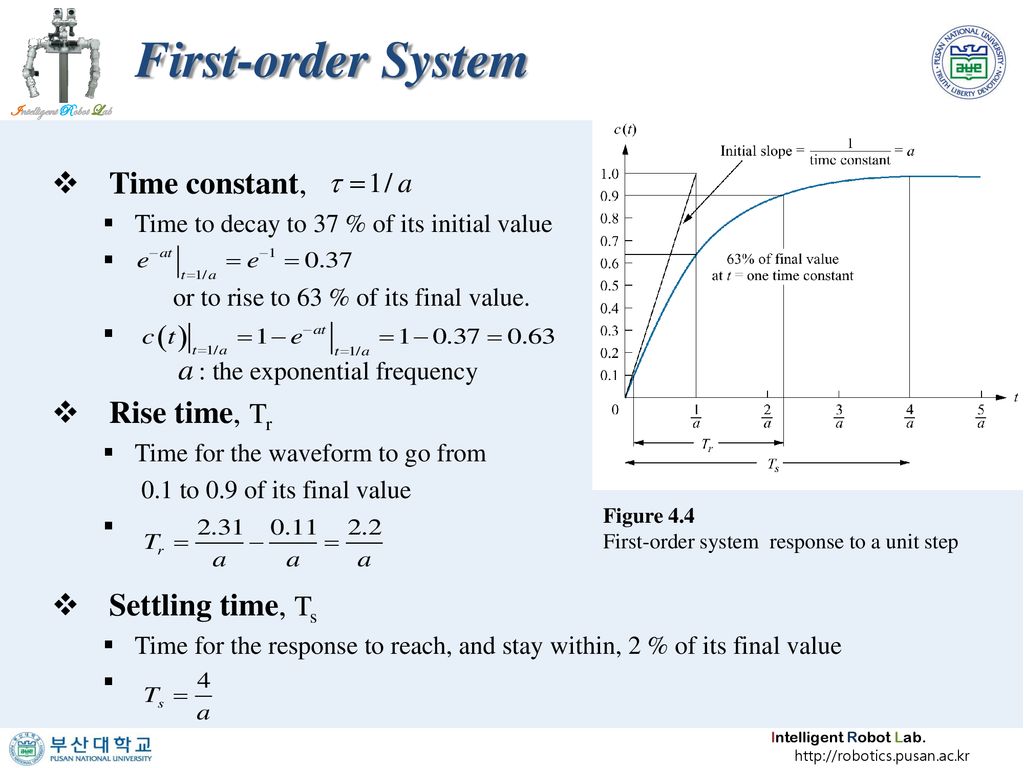
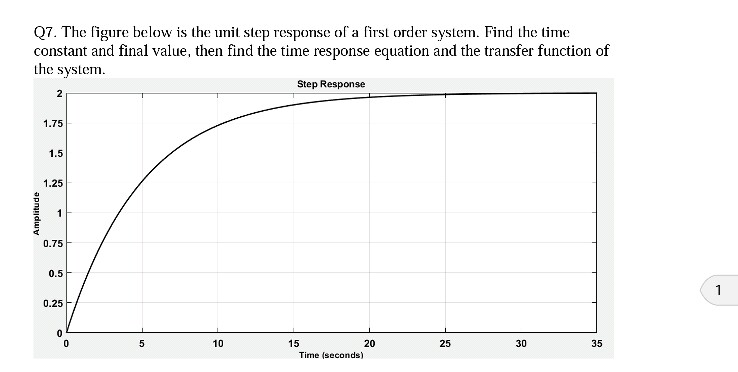
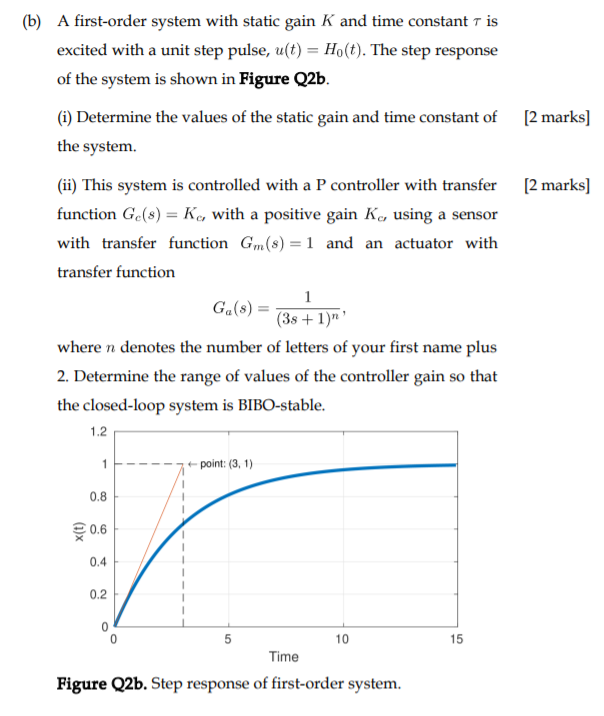
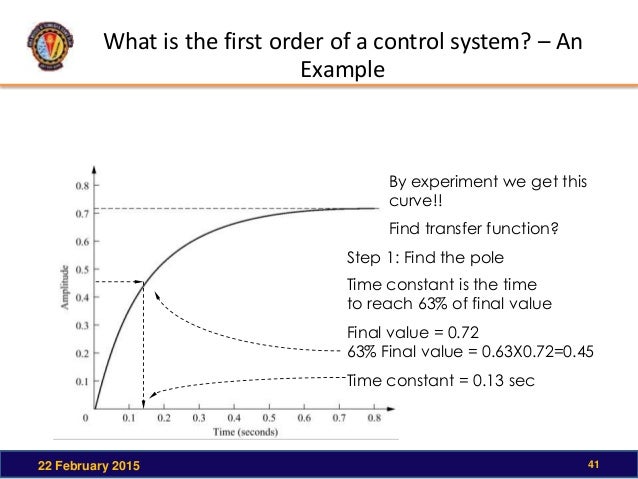
Determines the gain and the time constant for a stirred tank bioreactor that is represented by a first-order transfer function. Ask Question Asked 9 years 1 month ago. Next consider what happens to the function when the elapsed time is equal to one time constant. The time constant of the system is the parameter T given by T1a. Thus when one time constant has elapsed the process output will have achieved 632 of its final value in the plot 126. And finally use the formula that you have stated. This form is convenient for representing a first order system in terms of its time constant and steady state gain. Consider the equation C s 1 s T 1 R s Substitute R s value in the above equation. Gs 3 s 2 15 05s 1 a 0 2.
T is the time constant. The time constant is given by T 1 ζ ω n. T is the time constant. This is true of all first order systems. T F a s 2 2 ζ ω n s ω n 2. ES 205 Summer 2014 Agenda Time estimates Item 30 min Determining the time constant using the log-incomplete response method 15 min Organize for using the apparatuses 145 min Lab tasks 1. Refers to the time required for the physical quantity to decay from the maximum value to 1e of the maximum value.























Post a Comment for "Time Constant First Order System"